

Thus the males are ZZ and the be males are ZW. To prevent cove fusion with the X and Y chromosomes convention, we designate the sex chromosomes in these organism as Z and W. The male in there organisms is the homogametic and the female is the heterogametic sex. In birds, butterflies, moths, and some fish, the sex chromosomes composition is the opposite of that in mammals. Not all organisms have an X-Y sex chromosome makeup, like that found in mammals and in Drosophila. I n human P ♀ 44 autosomes + XX x ♂ 44 autosomes + XYį 1 44 autosomes + XX x 44 autosomes + XY

The males having XY genotype are termed as heterogametes sex as they produce two kinds of games 50% of gametes X – chromosomes and 50% Y – chromosome. The females having XX genotype are called homage metic sex as they produce only one king of gametes.
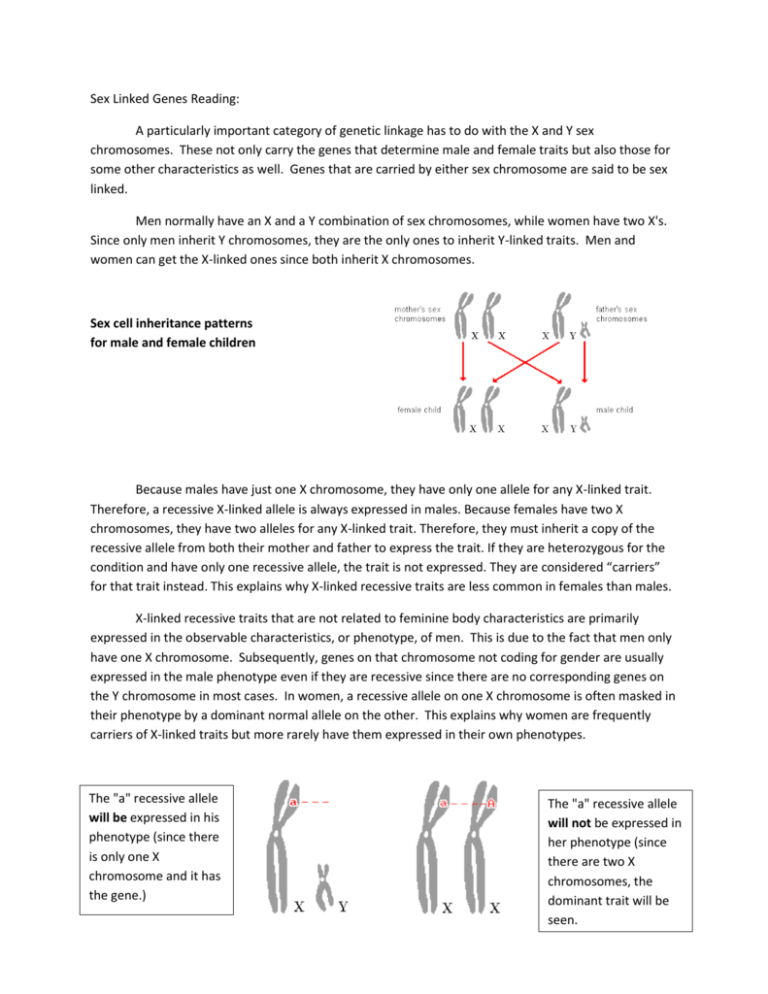
In human and the fruit fly, Drosophila me lake garter, for example has two X chromosome (she is XX with respect to the sex chromosomes) while the male has one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (he is XY). The sex chromosomes typically are designated the X chromosome, Y chromosome. For many animals the sex chromosome of the individual is directly related. The support the chromosome theory of inheritance came from experiments that related the hereditary behavior of particular genes to the transmission of the sex chromosome, the chromosome in eukaryotic that is represented, differently in the two sexes. This theory states that them chromosomes are the carriers of the genes. To explain this correlation, they proposed the chromosome theory of in heritance. In 1902 Walter Sutto and Theodor Boveri independently recognized that the closely paralleled the pattern of transmission of genes from one generation to the next closely paralleled the pattern of transmission of genes from one generation to the next. In 1900 Mendel’s work on the nature of heredity tiny factors was rediscovered. We know now, of course, that and a gene is a stretch of DNA that section of DNA contains information for a specific product: this.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
